Tag Archives: sql tutorials for beginners
MySQL Grant all privileges on database
MySQL Grant all privileges on database : GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES is used to grant the privileges on database in MySQL. We sometimes need to give the full privileges to the user on database. Here in this tutorial we are going to explain how you can grant all privileges on database to the users.
MySQL Grant all privileges on database
There are many ways to Grant all privileges to the user on any database. Here are some useful ways to grant the privileges on database in MySql.
MySQL Grant all privileges WITH GRANT OPTION
If you want to grant all privileges with grant option in mysql use the following Query –
mysql grant all privileges on database to user:
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON my_database.* TO 'my_user'@'%' WITH GRANT OPTION; |
This will give all privileges to the user my_user with grant option.
Here is another way to grant all privileges to the user.
MySQL Grant all privileges without GRANT OPTION
MySQL Grant all privileges to user identified by:
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON my_database.* to 'my_user@localhost' INDENTIFIED by 'my_passwd'; |
The above example will give the full PRIVILEGES to user identified by the password without grant option.
More About MySQL Grant Privileges
Let us learn more about the MySQL Grant Privileges. Let us give the selected Privileges to the user.
MySQL Grant SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, CREATE, DROP,INDEX, ALTER privileges to user
You can Grant SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, CREATE, DROP,INDEX, ALTER privileges simply using the below query on database.
MySQL Grant SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, CREATE, DROP,INDEX, ALTER :
GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, CREATE, DROP,INDEX, ALTER ON my_database.* TO 'my_user@localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'my_password'; |
The above example will give the SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, CREATE, DROP,INDEX and ALTER PRIVILEGES to the user on the database.
![]()
Can’t connect to local MySQL server through socket ‘/var/mysql/mysql.sock’
Can’t connect to local MySQL server through socket ‘/var/mysql/mysql.sock’ – Sometimes you get this error while starting the mysql server. There can be different reason for this. Here in this solution we are going to tell how you can fix the above error.
Can’t connect to local MySQL server through socket ‘/var/mysql/mysql.sock’
1 . Go to folder – /etc/mysql/ open my.cnf
2. Now go to client [client] section and add the following
If [Client] Section is not available-
Can’t connect to local MySQL server through socket :
[client] socket=/var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock |
If [Client] Section is available-
If client section is already available in my.cnf file then only add the below code in [client] section as below –
Can’t connect to local MySQL server through socket:
socket=/var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock |
After Adding the above it will fix your issue.
Get list of MySQL user accounts
Get list of MySQL user accounts : If you are looking to get the list of the user accounts in mysql you can get this simply using the query from mysql.user table. Here in this example we are going to explain how you can get all the users of the mysql using the simple query.
Get list of MySQL user accounts
Here is simple query which will give you the list of the MySql User Accounts –
Get list of MySQL user accounts:
SELECT User FROM mysql.user; |
The above example will give you the mysql users. It will produce output something like this –

More Information About MySql Users
Let us go over other detailed information from mysql.
MySql get Username, Password And Hostname
You can get the username, hostname and password from mysql simply using the query below –
MySql get Username, Password And Hostname (Hosts):
SELECT User, Password, Host FROM mysql.user; |
If you the above query it will give you the username, password and hostname. The output will be something like this –

SQL Prevent Duplicate INSERT – MySql
SQL Prevent Duplicate INSERT – MySql : If you are working with mysql insert operation and want to stop duplicate insertion operation . You can use INSERT IGNORE statement. This will prevent the duplicate row insertion.
SQL Prevent Duplicate INSERT – MySql
Here is an example of Insert ignore statement in mysql
SQL Prevent Duplicate INSERT – MySql
mysql> INSERT IGNORE INTO users (user_id, email) VALUES (32, test@ymail.com); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec) mysql> INSERT IGNORE INTO users (user_id, email) VALUES (32, test@ymail.com); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) |
The above example clearly shows when you run the same query to insert the same data it will not insert the data again.
Mysql create table primary key autoincrement example
Mysql create table primary key autoincrement example is explained below.
Sql create table with primary key
Example
CREATE TABLE Users ( ID int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, Name varchar(100), Email varchar(100), Address varchar(100), City varchar(100), PRIMARY KEY (ID) );
this will create table users with primary key ID and autoincrement functionality.
Sql create table with primary key
sql create table with primary key Syntax is explained below.
Sql create table with primary key with Syntax
Example
CREATE TABLE Users ( ID int, Name varchar(100), Email varchar(100), Address varchar(100), City varchar(100), PRIMARY KEY (ID) );
Which will create table users with primary key ID.
Mysql find duplicate records in table
Mysql find duplicate records in table
Syntax for MySQL find duplicate records in table
Simple Way to find the duplicate records in Sql is as
Select id Count( id ) As total_ids From Users Group By id Having Count( id) > 1 Order By total_ids desc;
Get last conversation in mysql table in facebook style
Get last conversation in mysql table in facebook style :
If you want to get conversation(chat) of users ie . the last message in the conversation use the following query it will give the last message in the conversation :
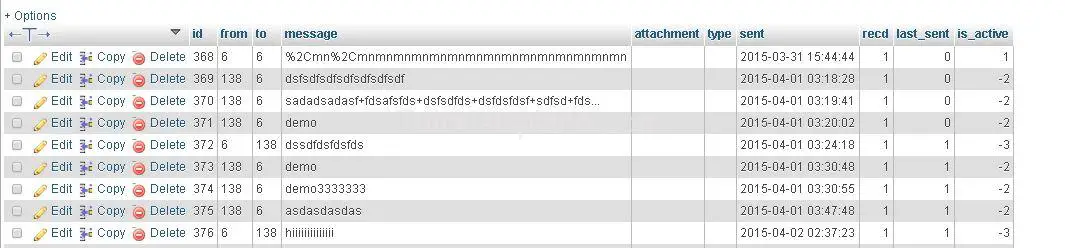
suppose you have following chat table
SELECT * FROM ( SELECT * FROM chat AS c WHERE c.from = '138' OR c.to = '138' ORDER BY c.id DESC ) AS m1 WHERE m1.is_active !=0 GROUP BY LEAST( m1.from, m1.to ) , GREATEST( m1.from, m1.to ) ORDER BY m1.id DESC LIMIT 0 , 10
Where c.to=2 or c.from=2 is current user’s id .
And is_active is deletion status.
SQL FOREIGN Key
SQL FOREIGN Key Constraint
A Foreign key is used to define the relation between two tables . A Foreign key points to the primary key in another table.
Suppose We Have The Following Tables :
Orders Table :
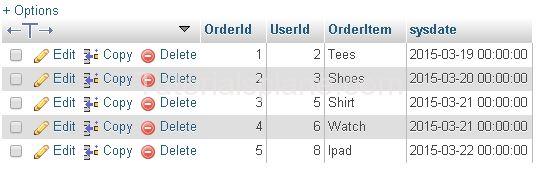
Note : “UserId” In “Orders” Table is the id of the users which is assigned to users in “Users” Table in “ID” column. The Values stored in “UserId” Column are referred from “Users” Table.
And
Users Table :
UserId In Orders table is the primary key in table Users ie . column ID(Primary Key).
Now to define this relation we have to make foreign key in Orders table.
There are Two Ways to Define Foreign Key :
1 . At the time of Creation of table :
Example
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS Orders (
OrderId int(11) NOT NULL,
UserId int(11) NOT NULL,
OrderItem varchar(100) NOT NULL,
Sysdate datetime NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT usersID_FOREIGN_KEY FOREIGN KEY (UserId)
REFERENCES Users(ID);
) ;
2 . In Existing table :
Example
ALTER TABLE Orders ADD
CONSTRAINT usersID_FOREIGN_KEY FOREIGN KEY (UserId)
REFERENCES Users(ID);
Delete Foreign Key Constraint :
Example
ALTER TABLE Orders DROP
CONSTRAINT usersID_FOREIGN_KEY;
Note : In Mysql Following Query Works.
Example
ALTER TABLE Orders DROP
FOREIGN KEY usersID_FOREIGN_KEY;