Category Archives: Sql
SQL – Like
SQL Like Clause
Like operator is used to filter the results . Like operator compares the results using the wild cards.
There are two types of wildcards used for the filtering & matching the result.
1. % – (Percent Symbol).
2. _ – (Underscore Symbol).
SQL Like CLause Syntax (Wildcard %)
SELECT columnName1, ColumnName2.. FROM TableName WHERE ColumnName LIKE ‘%Pattern’;
Or
SELECT columnName1, ColumnName2.. FROM TableName WHERE ColumnName LIKE ‘Pattern%’;
or
SELECT columnName1, ColumnName2.. FROM TableName WHERE ColumnName LIKE ‘%Pattern%’;
Explanation :
‘Pattern%’ – : Mathes & finds the pattern where column value starts with the provided pattern (Ex . – ‘%John’ – Will find the records where Name(Column) starts with ‘John’).
‘%Pattern’ – : Mathes & finds the pattern where column value ends with the provided pattern (Ex . – ‘John%’ – Will find the records where Name(Column) ends with ‘John’ ).
‘%Pattern%’ – : Mathes & finds the pattern where pattern find at any place in column value (Ex . – ‘%John%’ – Will find the records where Name(Column) find at any where ).
SQL Like CLause Syntax (Wildcard _ ) –
SELECT columnName1, ColumnName2.. FROM TableName WHERE ColumnName LIKE ‘_Pattern’;
Or
SELECT columnName1, ColumnName2.. FROM TableName WHERE ColumnName LIKE ‘Pattern_’;
or
SELECT columnName1, ColumnName2.. FROM TableName WHERE ColumnName LIKE ‘_Pattern_’;
Explanation :
‘_Pattern’ – : Mathes & finds the pattern where column value has the pattern at second place (Ex . – ‘_J’ – Will match the column value where second value is ‘J’).
‘Pattern_’ – : Mathes & finds the pattern where column value start with the pattern (Ex . – ‘J%’ – Will match the column value where column value starts with ‘J’ ).
‘_Pattern_’ – : Mathes & finds the pattern where pattern where (Ex . – ‘_Jn_’ – Will find the records where 2nd value is ‘J’ and seond last value is ‘n’ ).
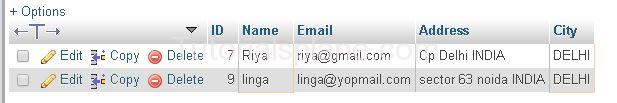
Example :
Example
Will Produce The Follwoing Result.
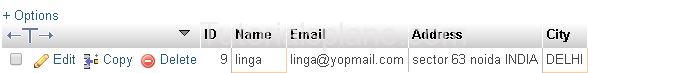
Example :
Example
Will Produce The Follwoing Result.
SQL – DELETE
SQL DELETE Query
SQL – DELETE Query is used to delete records(rows) from table.
SQL DELETE Syntax :
DELETE FROM TableName WHERE columnName = someColumnValue;
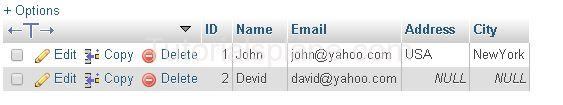
Suppose We Have Following Data :
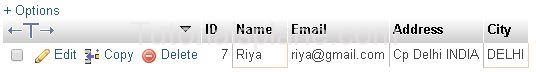
Example : We want to delete row where id is ‘9’
Example
This Will Delete the row where id is ‘9’ . The Table will look Now :
SQL – UPDATE
SQL Update Query
SQL – UPDATE Statement is used to update or change the records in table which are existing in the table.
SQL Update Query with Syntax
SET columnName1 = newValue1,
SET columnName2 = newValue2,
SET columnName3 = newValue3
WHERE columnName = someColumnValue;
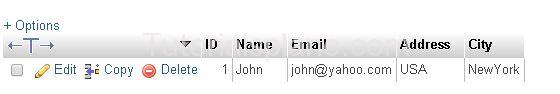
Suppose We have Following Data :
Update Example :
Example
The Above Query Will Update the row where email is ‘david@yahoo.com’ the update data will be as :
SQL ORDER BY
SQL ORDER BY Clause
ORDER BY Clause is used to sort the data on the basis of columns in ascending or descing order.
SQL ORDER BY Syntax
:
from TableName ORDER By columnName1 , columnName2 ASC | DESC
Note : If We do not use the ASC or DESC keyword the Default order ASC is considered.
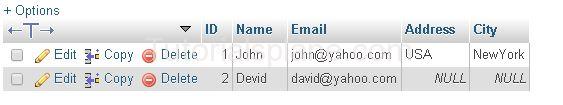
Suppose We Have The Following Data :
ORDER BY DESC Example :
Example
The Above Query Will Sort the result in descening order by Id. The Query Produces the result as :
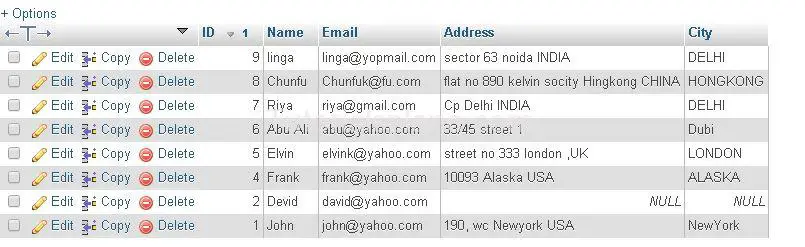
ORDER BY ASC Example :
Example
The Above Query Will Sort the result in ascending order by Id. The Query Produces the result as :
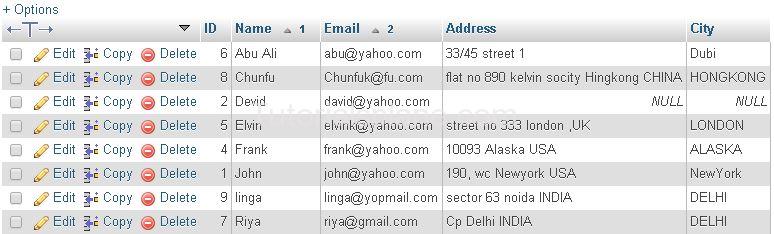
ORDER BY Multiple Columns Example :
Example
The Above Query Will Sort the result in ascending order by Name & Email. The Query Produces the result as :
SQL – AND & OR
SQL – AND & OR Clauses
SQL – AND & OR Explained
AND Clause :
And Clause displays the results where both the conditions are fullfilled.
OR Clause :
OR Clause displays the results where atleast one conditions is fullfilled.
Suppose we have following data :
AND Clause Example :
Example
Where [City=”DELHI” and Name=’Riya’] Both Conditions are satisfied.
This Will Produce The Result As :
OR Clause Example :
Example
Where [City=”DELHI” OR Name=’Riya’] Either condition is satisfied.
This Will Produce The Result As :
AND & OR Clause Together Example :
This will select the result where city is (“delhi” or name is “riya” )[produces two rows]
with the condition followed by name “linga” [Selects one from the two rows where name is “linga”]
Example
This Will Produce The Result As :
SQL – WHERE Clause
SQL WHERE Clause
SQL WHERE Clause is used to filter the recoreds on the basis of some condition.
This will fetch the results which will fullfill the condition specified.
SQL WHERE Syntax :
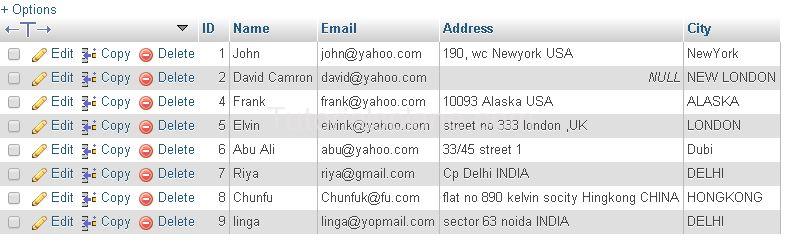
Suppose The “Users” Table has following records :
Suppose we have to find those records which have ‘city’ value as “DELHI”
Example 1 – : The Following Example will fetch the results as
Example
The Above Query Will Fetch the results :
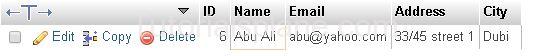
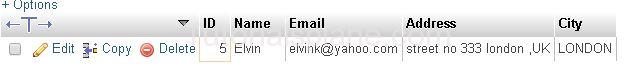
Example 2 – : Fetch The Results where user’s ID is ‘5’
Example
The Above Query Will Produce the result as :
SQL – SELECT
SQL – SELECT Statement :
Sql Select Statement is used to fetch records from database table.
SQL – SELECT Syntax 1 (Select All Columns) :
SQL – SELECT Syntax 2 (Select few Columns) :
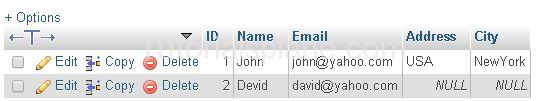
SQL Select All Columns Example :
Example
The above Query will display the results as :
SQL Select Few Columns Example :
Example
The above Query will display the results as :
SQL – INSERT
SQL – INSERT Statement:
SQL INSERT INTO Statement is used to insert a new row(ie. record) in a table.
SQL INSERT INTO Syntax:
Note: The Above Syntax inserts rows in all columns of the table.
If You want to insert values in selected columns the following syntax is used :
EXAMPLE 1 (Insert in all column) :
Example
1 New row will be inserted.
Now the table has its first record after the selection it will show:
EXAMPLE 2 (Insert in few columns only):
Example
Note: We need to specify the column name in which we want to insert values Like If want to insert values in ID, Name and Email Columns only…
Now the table will look like:
SQL – CREATE TABLE
SQL Create Table Syntax is used to create a table in database .
Tables are collection of rows & columns.
SQL – CREATE TABLE Syntax
(
ColumnName1 datatype,
ColumnName2 datatype,
ColumnName3 datatype,
….
….
….
);
ColumnName1, ColumnName2, ColumnName3, .. are name of columns.
datatype specifies the type of data to be stored in that column example : integer, variable , text or decimal etc..
SQL – CREATE TABLE Example
Example
(
ID int,
Name varchar(100),
Email varchar(100),
Address varchar(100),
City varchar(100),
PRIMARY KEY (ID)
);
* PRIMARY KEY : Primary creates constraint on the column ID which will contain unique & not null values. We will Explain it in later topics.
Users Table will be created in CustomersDb.
To Verify the table Creation Use The following Command .
Example
Which will Display Created table AS :